Types of Root Canal X-Rays: Uses, Advantages, and Disadvantages
When it comes to diagnosing and treating root canal issues, X-rays play a crucial role in providing dentists with a clear view of the tooth’s internal structure. There are several types of X-rays used in root canal procedures, each serving a specific purpose. Here’s a closer look at the different types, along with their uses, advantages, and disadvantages.
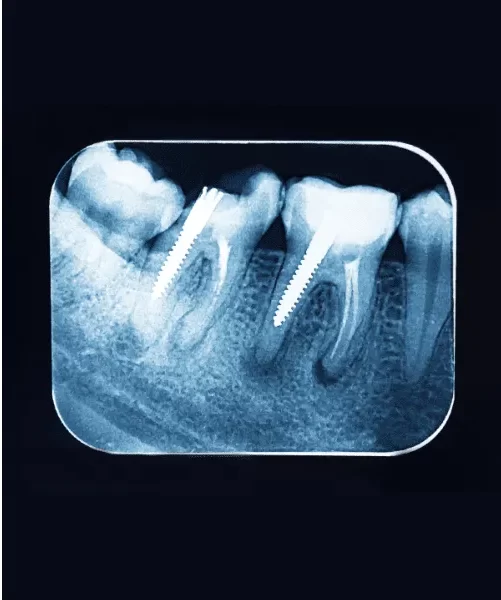
1. Periapical X-Rays from Types of Root Canal X-Rays
Uses:
Periapical X-rays are the most common type used during root canal procedures. They focus on capturing the entire tooth, from the crown to the root tip, and the surrounding bone. Dentists use these X-rays to diagnose abscesses, bone loss, and other issues at the root level.
Advantages:
- Provides a detailed image of the tooth and surrounding bone.
- Helps in detecting infections, cysts, and fractures.
- Essential for confirming the success of the root canal treatment.
Disadvantages:
- Limited to a small area, requiring multiple X-rays for comprehensive diagnosis.
- Slight discomfort due to the placement of the X-ray film or sensor in the mouth.
2. Bitewing X-Rays from Types of Root Canal X-Rays
Uses:
Bitewing X-rays are commonly used to detect cavities between teeth, but they can also provide useful information during root canal procedures. They show the crowns of the upper and lower teeth in a specific section of the mouth.
Advantages:
- Useful for identifying decay and infections in the crown area.
- Provides a good overview of the tooth’s structure above the gum line.
Disadvantages:
- Does not capture the entire tooth, especially the root area.
- Limited use in diagnosing root canal-specific issues.
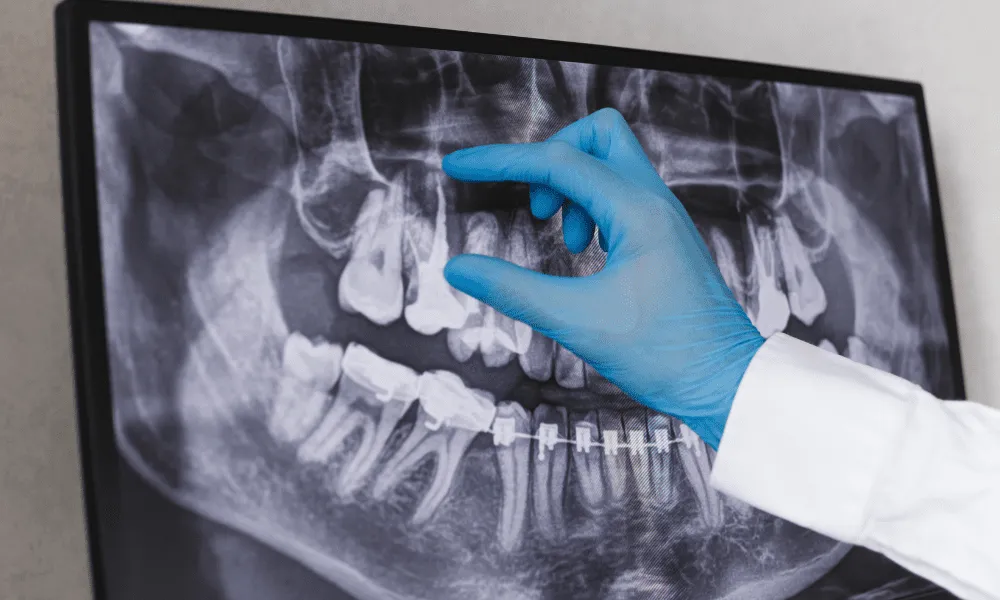
3. Panoramic X-Rays
Uses:
Panoramic X-rays provide a broad view of the entire mouth, including all the teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures. While not as detailed as periapical X-rays, they are useful for initial assessments and planning complex dental procedures.
Advantages:
- Covers a larger area, offering a complete view of the mouth.
- Helpful in identifying impacted teeth, cysts, tumors, and jaw issues.
Disadvantages:
- Lower resolution compared to periapical X-rays, which may miss small details.
- Not ideal for detailed examination of individual teeth and roots.
4. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
Uses:
CBCT scans provide a 3D image of the tooth and surrounding tissues. This advanced imaging technique is particularly useful for complex root canal cases, such as those involving multiple canals or unusual anatomy.
Advantages:
- Offers a comprehensive 3D view, revealing the tooth’s internal structure in detail.
- Essential for diagnosing difficult-to-detect issues, such as additional canals or root fractures.
- Helps in planning precise treatment strategies.
Disadvantages:
- Higher radiation exposure compared to standard X-rays.
- More expensive and less commonly available than other types of X-rays.
- May require specialized equipment and expertise to interpret the results.
Each type of root canal X-ray has its unique applications, benefits, and limitations. Understanding these differences helps both patients and dental professionals choose the most appropriate imaging technique for accurate diagnosis and successful treatment. Whether it’s the detailed view provided by periapical X-rays or the comprehensive 3D imaging of a CBCT scan, these tools are indispensable in ensuring the best possible outcome for root canal therapy.
Also read: SC Joint X-ray Positioning